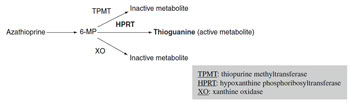
Azathioprine (Imuran) | | Figure 7.1 Metabolic pathway for azathioprine |
(Figure 7.1) - Purine analogue which blocks purine synthesis (S-phase-specific); active metabolite is 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) which is converted to either inactive or active metabolite (6-thioguanine) via one of three enzymatic pathways (TPMT, HPRT, XO):
- If XO or TPMT activity inhibited, HPRT becomes primary pathway causing excess toxic purine analogues, which can cause bone marrow suppression; can occur if azathioprine used with allopurinol (which blocks XO) or in patients with genetically low TPMT levels
- Excreted by kidneys
- Check TPMT levels before starting medication
- SE: bone marrow suppression, hypersensitivity syndrome, teratogenicity, lymphoproliferative malignancies (latter only documented in rheumatoid arthritis)
- Pregnancy category D
|