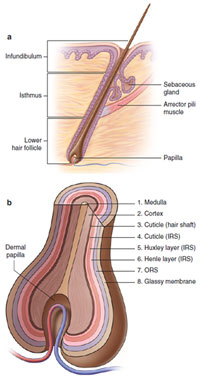
Hair | Figure 1.5 A: Longitudinal
section of hair follicle, B: Cross-
section of hair follicle |
- Hair follicle is positioned at an angle; base of follicle typically within the subcutaneous fat
- Longitudinal anatomy (Figure 1.5A):
- Infundibulum: upper portion of follicle extending from surface of epidermis to opening of sebaceous gland
- Isthmus: middle portion extending from opening of sebaceous gland duct to insertion of arrector pili muscle (bulge), lined by outer root sheath (ORS), no inner root sheath (IRS)
- Inferior segment or lower hair follicle: extending from base of isthmus to hair bulb; consists of matrix cells and envelops dermal papilla; lined by IRS; ORS present but not keratinized; widest diameter termed critical line of Auber (below this is where bulk of mitotic activity occurs); melanocytes in bulb provide melanosomes for hair color
- Cross-sectional anatomy (Figure 1.5B) from outer to inner layer:
- Glassy membrane → ORS → Henle’s layer (IRS) → Huxley’s layer (IRS) → cuticle (IRS) → hair shaft cuticle → cortex → medulla
- Important sites:
- ORS: extends entire length of hair follicle; undergoes trichilemmal keratinization (no keratohyalin granules) in isthmus but changes to normal epidermal keratinization (with KHG) in infundibulum; ORS basal layer contiguous with keratinizing epidermal cells
- IRS: cuticle of IRS interlocked with cuticle of hair shaft; IRS is present until bulge area, at which point it disintegrates; contains KHG in cytoplasm
- Cortex: contains majority of hair keratins; cuticle maintains integrity of hair fibers
- Bulge: thickened area of follicle wall, contains stem cells; insertion site of arrector pili
- Dermal papilla: collection of mesenchymal cells which protrudes into hair bulb
- Different hair cycles (not synchronous): anagen → catagen → telogen
- Anagen: hair growth phase, duration of phase determines length of hair, duration 2–6 years on scalp; 85% of hairs in this cycle at any one time
- Catagen: transitional phase (regression); bulb regresses and IRS lost, 2–4 week duration on scalp; 2% hairs in this cycle
| | | | | | Telogen: resting or “ tired” phase | | | | | |
|
- Growth: 0.4 mm/day, 1.2 cm/month
- Average number of hairs on scalp: 100,000 (new follicles cannot develop in adult skin); 100 hairs normally lost each day
- Curly versus straight hair depends on shape of follicle (round follicle results in straight hair, oval follicle in curly hair)
- Proteins containing sulfur impart stability in keratins within the hair shaft (disulfide bonds)
- Melanocytes found in matrix area of follicle and pigment production coupled with anagen phase; no melanin formation in telogen and catagen phase
|