Stratum Spinosum| | | | | | Flegel’s disease, Harlequin ichthyosis: ↓ lamellar granules (LG)
X-linked ichthyosis: absent steroid sulfatase in LG
Congenital ichthyosiform erythrodermaa: ↑ LG but structurally abnormal | | | | | |
|
- New synthesis of K1/K10; K5/14 still present (not de novo)
- Cells contain lamellar granules (syn: lamellated bodies or odland bodies): intracellular lipid-carrying granules formed w/in Golgi in upper spinous layer; contain glycoproteins and lipid precursors which are discharged into intercellular space between granular and cornified layer; forms lamellar sheets (ceramide) or “mortar” which acts as intercellular cement for corneocytes (“bricks”), thus contributing to formation of cutaneous lipid barrier
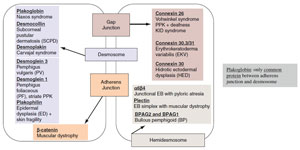
- Types of cell junctions prominently seen in this layer and in granular layer:
- Desmosomes: calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion molecules between keratinocytes; serve as attachment sites for cytoskeleton (intermediate filaments); each desmosome made up of several proteins:
- Transmembrane proteins: desmoglein 1/3, desmocollin 1/2 (desmosomal cadherins)
- Desmosomal plaque proteins: plakoglobin (γ - catenin), desmoplakin 1/2, keratocalmin, desmoyokin, band 6 protein, envoplakin
- Adherens junctions (zonula adherens): transmembrane classical cadherins (namely E and P) linked to actin cytoskeleton via cytoplasmic plaque proteins (α, β, γ - catenin)
| Figure 1.1 Skin diseases associated with cell
junctions |
- Gap junctions: transmembrane channels formed by six connexin monomers, allows for cytoplasmic continuity and communication between cells
- Know particular diseases associated with defects or antibodies against certain cell junction proteins (Figure 1.1)
|